Contents
- What is Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
- What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
- CVI vs DVT: Key Differences
- Symptoms: DVT Symptoms vs Venous Insufficiency Symptoms
- Diagnosis: How Are CVI and DVT Identified?
- Treatment Options for CVI and DVT
- Living with Chronic Venous Disease: Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Empowering Patients to Make Informed Decisions
- Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to vein health, two conditions often cause confusion: chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Both affect the veins in your legs, but they are very different in how they develop, the risks they pose, and how they’re treated.
CVI happens when blood has trouble flowing back up to the heart, leading to pooling, swelling, and discomfort. DVT, on the other hand, involves a blood clot deep in the vein—something that can quickly become life-threatening if left untreated.
Knowing the difference between these two conditions can make all the difference in recognizing symptoms early and getting the right care. Let’s break down what sets them apart, what signs to watch for, and when to seek medical attention.
What is Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
CVI is a condition affecting blood return to the heart from the legs. It occurs when vein valves become weak or damaged, causing blood to pool in the lower extremities. This leads to increased pressure in the veins.
People with CVI often experience uncomfortable symptoms. Common signs include swelling, aching, and heaviness in the legs. These symptoms may worsen after long periods of standing or sitting. Skin changes and varicose veins are also frequent indicators of this condition.
Several factors contribute to the development of CVI. Key risk factors include:
- Advanced age
- Family history of vein conditions
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Prolonged periods of immobility
Early diagnosis and management of CVI are important to prevent complications. Left untreated, chronic venous disease can significantly affect a person’s quality of life. Management strategies focus on improving blood flow and alleviating symptoms.
Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and leg elevation, are often recommended. Compression stockings and minimally invasive procedures can also effectively manage CVI. Consulting with a vein and vascular specialist is crucial for determining the best treatment plan.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
DVT is a serious vein condition. It occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This condition can pose significant health risks.
Understanding DVT is vital for timely intervention. DVT is particularly dangerous due to its potential complications. A clot may break free and travel to the lungs, leading to a pulmonary embolism. This condition is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
DVT is often associated with specific risk factors. These include:
- Prolonged immobility
- Recent surgery or trauma
- Cancer
- Pregnancy
- Inherited clotting disorders
Symptoms of DVT can vary in severity. They may include swelling and pain in the affected leg. Additionally, tenderness, warmth, and redness might be present. However, DVT can sometimes occur without visible symptoms.
Accurate diagnosis of DVT is crucial to prevent complications. Healthcare professionals typically use ultrasound imaging and blood tests for this purpose. Early detection allows for effective treatment, reducing the risk of dangerous outcomes. Treatment focuses on preventing clot growth and lowering the risk of complications. Anticoagulant medications and lifestyle changes are often recommended to manage DVT effectively.
CVI vs DVT: Key Differences
Chronic Venous Insufficiency and Deep Vein Thrombosis affect veins. Yet, they differ significantly in causes and impacts. Understanding these differences is critical for proper management.
CVI arises from improper blood flow back to the heart. It results in increased venous pressure and blood pooling. DVT, by contrast, involves a clot forming within a deep vein. This makes DVT potentially life-threatening.
Symptoms also help distinguish these conditions. CVI typically presents with leg swelling, pain, and skin changes. Varicose veins are common. DVT symptoms might include swelling and pain, but also redness and warmth.
Despite differences, both conditions require medical care. Effective management can prevent complications. Understanding these distinctions empowers patients to seek timely treatment. For many, it’s the key to improving vein health and quality of life.
Symptoms: DVT Symptoms vs Venous Insufficiency Symptoms
Recognizing symptoms can aid in distinguishing DVT from CVI. Each has unique indicators but they can appear similar. This may cause confusion. Understanding these symptoms helps in seeking appropriate care.
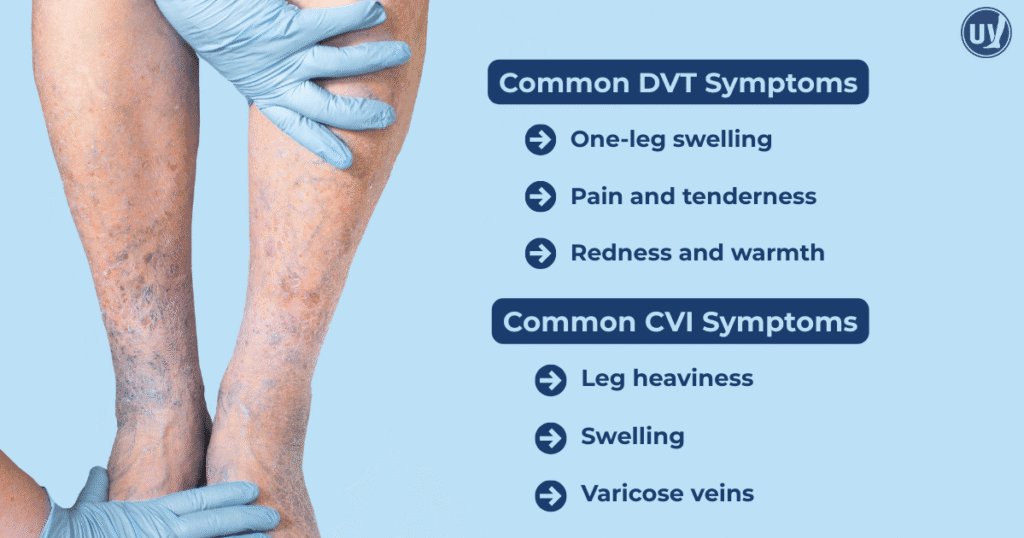
DVT symptoms tend to be more acute. They often include swelling, usually in one leg. You might notice pain or tenderness. Redness and warmth around the affected area are also common.
In contrast, CVI symptoms can be more chronic. They develop slowly over time. Common signs include a heavy feeling in the legs, particularly after standing. Swelling is also frequent, alongside varicose veins.
These symptoms are crucial cues. They guide healthcare providers in making accurate diagnoses. Recognizing them can prompt timely intervention. This helps prevent complications, improving health outcomes.
Diagnosis: How Are CVI and DVT Identified?
Diagnosing CVI and DVT involves different techniques. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. While both conditions affect veins, their diagnostic approaches vary.
For CVI, doctors often begin with a detailed physical examination. This helps in observing symptoms like skin changes and varicose veins. An ultrasound might be used to assess blood flow and identify any valve issues.
For DVT, more immediate actions are taken. Doctors might use a combination of:
- Ultrasound imaging to locate blood clots
- D-dimer blood tests to check for clotting activity
- Venography in complex cases
Recognizing the methods used for each condition helps in understanding the process. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications. Accurate evaluation ensures that patients receive the appropriate care and management.
Treatment Options for CVI and DVT
Managing CVI involves multiple strategies. Early intervention can alleviate symptoms and prevent progression. Treatment often aims to improve blood flow and relieve discomfort.
DVT requires swift action. Preventing clot enlargement and reducing risks of complications are priorities. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the condition.
Each condition necessitates a tailored approach to care. Collaboration with healthcare providers ensures optimal treatment choices. Understanding these options empowers patients to manage their vein health effectively.
Living with Chronic Venous Disease: Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
Living with chronic venous disease requires proactive management. Daily habits play a vital role in maintaining vein health. Simple lifestyle changes can significantly improve quality of life.
Eating a balanced diet helps in weight management. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on veins. Stay hydrated to keep blood circulation optimal.
It’s essential to wear clothing that doesn’t restrict blood flow. Loose-fitting clothes encourage better circulation. Prioritize these lifestyle adjustments for improved vascular health over time.
When to Seek Medical Help
It’s crucial to recognize when medical intervention is necessary. Seek medical advice if you experience sudden leg swelling, severe pain, or changes in skin color.
Prompt action ensures better outcomes. Don’t delay if you notice signs of DVT or worsening symptoms of CVI. Early treatment can prevent serious complications.
Empowering Patients to Make Informed Decisions
Understanding the differences between chronic venous insufficiency and DVT is more than medical knowledge—it’s the foundation for protecting your health. Recognizing symptoms early and knowing when to seek care can make all the difference in your treatment and peace of mind.
If you’ve noticed leg pain, swelling, or other concerning symptoms, don’t wait. Schedule a consultation with UVVC today and take the first step toward better vein health.
Frequently Asked Questions
CVI is caused by weakened vein valves that lead to blood pooling, while DVT involves a blood clot in a deep vein, often in the legs.
Yes. If untreated, a clot from DVT can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism. Prompt medical care is critical.
While CVI does not directly cause DVT, both share risk factors like poor circulation and vein damage. A specialist can evaluate your risks.