Contents
- Understanding Cholesterol: Types and Functions
- How High Cholesterol Affects Blood Vessels
- The Link Between Cholesterol and Vascular Disease
- High Cholesterol and Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
- Does High Cholesterol Cause Leg Pain?
- Risk Factors and Who Is at Risk
- Diagnosing High Cholesterol and Vascular Disease
- Managing and Lowering Cholesterol for Vascular Health
- Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Vascular Disease
- Taking Charge of Your Vascular Health
- Frequently Asked Questions
Cholesterol is essential for our bodies—it helps build cells, produce hormones, and keep our systems running smoothly. But when levels get too high, it can become a silent threat to vascular health. Excess cholesterol can contribute to serious conditions like peripheral arterial disease (PAD), which may cause leg pain and limit mobility.
Understanding how cholesterol affects your vascular system is the first step in prevention and effective management. From lifestyle choices to medical treatments, there are ways to protect your arteries and support long-term vascular health. In this article, we’ll explore the critical link between cholesterol and vascular disease, helping you take charge of your circulation and overall wellbeing.
Understanding Cholesterol: Types and Functions
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in the blood. It’s essential for building healthy cells and hormones. However, not all cholesterol is the same.
There are two primary types of cholesterol: LDL and HDL. LDL, or low-density lipoprotein, is often termed “bad” cholesterol. It contributes to the buildup of plaque in arteries.
HDL, or high-density lipoprotein, is known as “good” cholesterol. It helps remove LDL from the bloodstream and prevents blockages.
Maintaining a balance between these types is crucial. High LDL levels can lead to conditions like atherosclerosis. This, in turn, poses risks to vascular health. Hence, monitoring cholesterol types is important for preventing vascular diseases.
How High Cholesterol Affects Blood Vessels
High cholesterol, particularly high LDL, can significantly impact blood vessels. LDL tends to deposit cholesterol in arterial walls.
This accumulation results in plaque formation. Over time, plaques harden and narrow the arteries. This process is known as atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis can obstruct blood flow, leading to vascular diseases. These blockages can cause serious complications, including heart attacks and strokes.
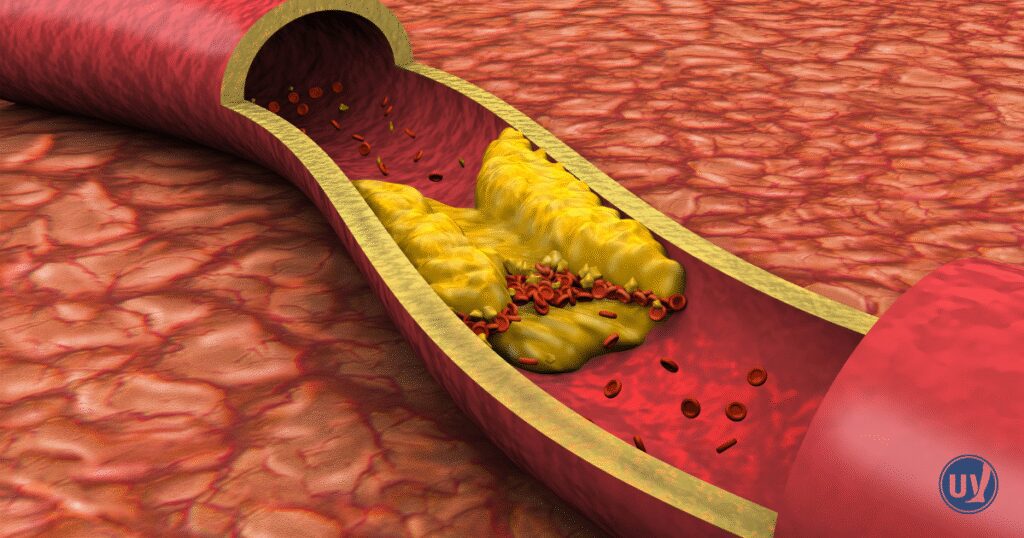
Key impacts of high cholesterol on blood vessels include:
- Plaque Buildup: Thickens artery walls.
- Narrowed Arteries: Reduces blood flow.
- Increased Blood Pressure: Forces heart to pump harder.
When blood flow is obstructed, tissues may not get enough oxygen. This can manifest as symptoms in various parts of the body.
Managing cholesterol effectively can prevent these harmful effects on blood vessels. Early intervention is crucial to mitigating long-term risks. Understanding these impacts is vital for overall vascular health management.
The Link Between Cholesterol and Vascular Disease
Cholesterol plays a central role in vascular disease development. High levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to plaque accumulation in arteries. This buildup narrows and stiffens the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of vascular diseases, impacting heart and peripheral blood vessels. As plaque grows, it can restrict or block blood flow. This obstruction increases the risk of severe complications like heart attacks.
Research continues to explore this complex relationship. Genetics, lifestyle, and other health conditions can influence cholesterol levels and vascular disease risk. High cholesterol often acts silently, underscoring the need for awareness and proactive management. Regular health screenings and lifestyle modifications can help mitigate the risks associated with high cholesterol and vascular disease. Understanding these links empowers individuals to better manage their cardiovascular health.
High Cholesterol and Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Peripheral arterial disease primarily affects blood vessels outside the heart and brain. High cholesterol is a major risk factor for PAD development. LDL cholesterol contributes to artery narrowing, restricting blood flow to limbs, often the legs.
The symptoms of PAD vary but typically worsen with activity. You may experience:
- Leg Pain: While walking or exercising.
- Cramping: Occurs in calves or thighs.
- Fatigue: Muscle weakness or tiredness.
These symptoms commonly indicate claudication, related to reduced limb blood flow. As the disease progresses, symptoms may become more persistent. High cholesterol management can delay or halt PAD progression.
Lifestyle adjustments are crucial for managing and preventing PAD. Physical activity, a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking can improve outcomes. Medical treatments, including cholesterol-lowering drugs like statins, may be necessary.
Routine check-ups help detect PAD early and initiate timely treatment. Understanding high cholesterol’s impact on PAD emphasizes the need for proactive cardiovascular care. Addressing these risk factors can significantly enhance life quality and reduce complications associated with PAD.
Does High Cholesterol Cause Leg Pain?
High cholesterol can indeed cause leg pain, especially in individuals with peripheral arterial disease. The accumulation of LDL cholesterol leads to plaque formation in leg arteries. This plaque narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow to leg muscles.
Inadequate blood supply causes the leg muscles to cramp and ache. This pain is particularly noticeable during physical activities like walking. Known as claudication, this discomfort results from insufficient oxygen reaching the muscles.
Managing cholesterol levels can alleviate leg pain and improve circulation. Medications like statins and lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, are essential strategies. Recognizing the link between high cholesterol and leg pain can prompt timely medical intervention, preventing more severe complications.
Risk Factors and Who Is at Risk
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing high cholesterol and vascular disease. Some factors are within your control, while others are not. Understanding these can help in assessing personal risk and taking preventative steps.
Genetics play a significant role, determining your body’s cholesterol levels. If high cholesterol runs in your family, you may be more prone. Age is another factor, as cholesterol levels typically rise as you get older.
Lifestyle choices also greatly impact cholesterol levels. Notable risk factors include:
- Unhealthy Diet: High in saturated and trans fats.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity.
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and lowers good cholesterol.
Addressing modifiable risk factors, such as diet and activity, can help manage cholesterol levels. Identifying these risks early helps tailor an effective strategy to maintain vascular health.
Diagnosing High Cholesterol and Vascular Disease
Diagnosing high cholesterol and vascular disease often starts with a simple blood test. This test measures LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, offering insight into your heart health.
To assess vascular disease, doctors may use additional tests. These can help determine the health of your blood vessels and circulation. Some common methods include:
- Ultrasound: Checks blood flow and artery condition.
- Angiography: Uses X-rays and dye to view blood vessels.
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI): Compares blood pressure in the ankle and arm.
Early diagnosis is critical for managing and treating high cholesterol and vascular disease. Regular screenings can catch issues before they lead to severe complications.
Managing and Lowering Cholesterol for Vascular Health
Effectively managing cholesterol is key to improving vascular health. There are various strategies available to lower cholesterol levels. Each approach can contribute significantly to reducing vascular disease risk.
Dietary changes play a crucial role. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can lower LDL cholesterol. Reducing saturated fats also helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
Regular exercise is another essential component. Engaging in physical activity at least 150 minutes a week can boost HDL cholesterol. This “good” cholesterol helps remove LDL from the bloodstream.
Medications can be necessary for some individuals. Statins are commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol. However, medical advice is crucial before starting any medication.
Addressing lifestyle factors such as quitting smoking can significantly impact your cholesterol levels too. Consistent and comprehensive management can lead to substantial health improvements.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Vascular Disease
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits is vital in preventing vascular disease. Simple daily changes can significantly impact your vascular health.
Focus on a balanced diet to protect your arteries. Foods low in saturated fat, and rich in fiber, help reduce cholesterol. Incorporate more fruits, veggies, and whole grains into meals.
Physical activity is crucial for maintaining vascular health. Aim for regular moderate exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming. Exercise enhances circulation and reduces disease risk.
These changes support better vascular health and overall well-being.
Taking Charge of Your Vascular Health
Understanding the link between cholesterol and vascular disease empowers you to take proactive steps toward prevention. Managing cholesterol through lifestyle changes, medications, and regular check-ups can make a significant difference in your vascular health and overall wellbeing.
Partnering with experienced healthcare professionals ensures you have the guidance needed to monitor progress and make informed decisions. Schedule a consultation with UVVC today to assess your vascular health and take the first step toward a healthier tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Excess cholesterol can contribute to peripheral vascular disease (PVD), which narrows the arteries in your legs and reduces blood flow. This can lead to symptoms like leg pain, cramping, or fatigue, especially during physical activity.
Lifestyle changes such as eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking can help manage cholesterol. In some cases, medications prescribed by your healthcare provider may also be necessary.
If you experience leg pain, swelling, numbness, or other circulation-related symptoms, or if you have high cholesterol, a consultation with a vascular specialist can help assess your risk and develop a personalized prevention or treatment plan.


