Contents
- Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
- What Is Atherectomy?
- When Is Atherectomy Used for PAD?
- Types of Atherectomy Procedures
- The Atherectomy Procedure: Step-by-Step
- Benefits of Atherectomy for Peripheral Artery Disease
- Recovery and Aftercare
- Atherectomy vs. Other Peripheral Artery Treatments
- Is Atherectomy Right for You?
- Moving Forward with PAD Treatment
- Frequently Asked Questions
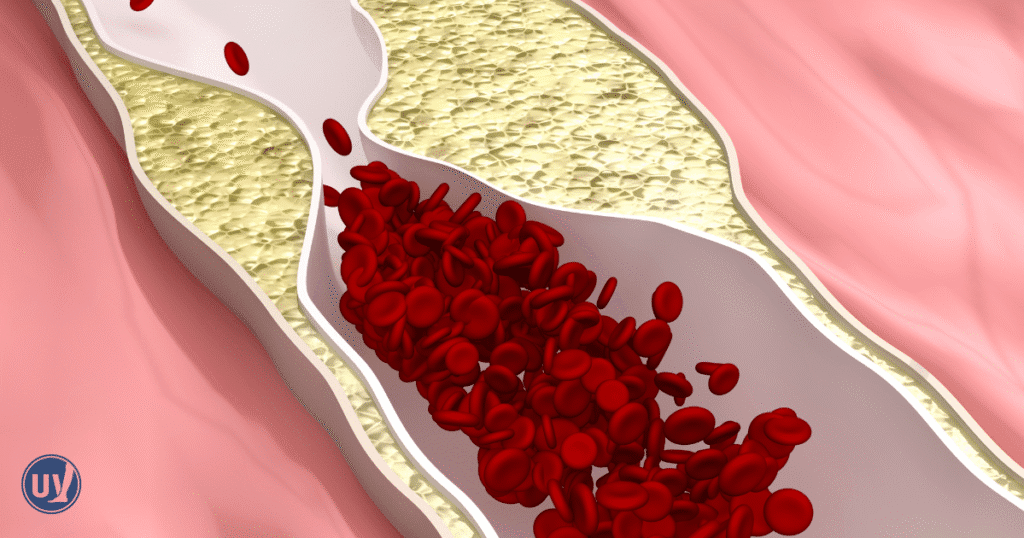
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a serious condition that develops when narrowed arteries restrict blood flow to the legs and feet. This reduced circulation can cause pain, cramping, and—in advanced cases—lead to significant complications.
Atherectomy is a minimally invasive treatment option that removes plaque buildup inside the arteries to restore healthier blood flow. It is often considered when other approaches, such as angioplasty or stenting, are not effective or appropriate.
Knowing when and why atherectomy may be recommended can help patients feel more confident in their care decisions. In this article, we’ll explain how the procedure works, outline its benefits and risks, and compare it with other treatments for PAD.
With the right information, you can better understand your options and take meaningful steps toward protecting your vascular health and improving your quality of life.
Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) affects millions globally. It occurs when arteries outside the heart or brain narrow due to plaque buildup. This restricts blood flow, primarily affecting the legs and feet.
Common symptoms of PAD include leg pain, cramping, and weakness while walking. This is often mistaken for normal aging but can indicate something more severe. If left untreated, PAD can lead to serious complications, such as critical limb ischemia or even limb loss.
PAD risk factors include smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Recognizing these can prompt early intervention, reducing the risk of complications.
Diagnosis often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and tests like the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI). The ABI compares blood pressure in the ankle and arm to assess blood flow.
Treatment focuses on improving blood flow and managing symptoms. It includes lifestyle changes, medication, and procedures like atherectomy. Understanding PAD empowers you to seek early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What Is Atherectomy?
Atherectomy is a minimally invasive procedure designed to remove plaque from arteries. This procedure is vital in treating PAD. By removing plaque, atherectomy enhances blood flow in the affected arteries, alleviating PAD symptoms like leg pain and cramping.
Different atherectomy devices are available, each suited for specific artery conditions. These devices can be rotational, directional, laser, or orbital. The choice of device depends on the plaque’s location and characteristics, ensuring optimal outcomes.
The procedure involves using a catheter to access the affected artery. The catheter’s design includes a specialized tip for cutting away or vaporizing plaque. This debris is then removed from the bloodstream, clearing the artery.
Atherectomy, often performed under local anesthesia in a hospital or outpatient setting, is favored for its reduced recovery time. Its efficacy is enhanced when combined with other treatments, such as angioplasty or stenting.
When Is Atherectomy Used for PAD?
Atherectomy is considered when other treatments for PAD are unsuitable. It offers a viable alternative when angioplasty or stenting has failed or isn’t recommended.
This procedure is often tailored to patients with complex plaques. These include those that are heavily calcified or located in hard-to-reach areas. For these challenging cases, atherectomy provides a precise method for plaque removal.
A vascular specialist may suggest atherectomy when symptoms severely impact daily life. Symptoms might include leg pain, cramping, or even non-healing wounds. Addressing these concerns can substantially improve the patient’s quality of life.
Types of Atherectomy Procedures
Atherectomy procedures come in various forms, each tailored to different arterial conditions. The choice depends on plaque characteristics and patient-specific factors. Understanding these can help determine the most suitable approach.
Four main types of atherectomy procedures are commonly used. These include:
- Rotational Atherectomy: Uses a rotating device to grind away plaque.
- Directional Atherectomy: Involves a cutting device to remove plaque in a specific direction.
- Laser Atherectomy: Employs laser energy to vaporize plaque.
- Orbital Atherectomy: Utilizes a diamond-coated crown to sand away plaque.
Each procedure has distinct advantages. Rotational atherectomy is often chosen for hard, calcified plaque. Directional atherectomy allows precise plaque removal. Laser atherectomy is effective for challenging plaque locations. Orbital atherectomy provides even plaque removal across the artery.
The decision on which type to use is made collaboratively with a healthcare provider. They assess factors like the plaque’s location and density, ensuring optimal outcomes. Patients are encouraged to discuss these options in detail, gaining a clearer understanding of their treatment pathway.
The Atherectomy Procedure: Step-by-Step
The atherectomy procedure is designed to be minimally invasive. It begins with your healthcare provider administering local anesthesia. This numbs the area and ensures your comfort during the procedure.
Once anesthesia takes effect, a small incision is made. Through this incision, a catheter is inserted into the artery. The catheter serves as a guide for the atherectomy device to reach the blocked site.
Imaging tools, like angiography, are used throughout the procedure. These help visualize the artery and ensure accurate navigation to the blockage. This step is crucial for the success of the atherectomy.
The specific atherectomy device then engages with the plaque. Depending on the type used, it may cut, sand, or vaporize the plaque away. The aim is to clear the blockage and restore blood flow effectively.
The entire procedure typically takes one to two hours. After plaque removal, the catheter and device are withdrawn carefully. Finally, the incision site is closed, concluding the procedure. Most patients can leave on the same day, commencing a swift recovery.
Benefits of Atherectomy for Peripheral Artery Disease
Atherectomy provides numerous benefits for patients dealing with Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). It’s a minimally invasive procedure, which means less pain and faster recovery compared to open surgery.
One of the primary benefits is the significant improvement in blood flow. By removing plaque, atherectomy alleviates symptoms like pain and cramping. This leads to enhanced mobility and overall quality of life.
This combination of benefits makes atherectomy an attractive option for many patients experiencing PAD symptoms.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery after an atherectomy procedure is often swift, allowing patients to resume daily activities soon. The procedure is minimally invasive, which contributes to a shorter recovery period. Most patients find they can get back to their regular routines within a few days.
Effective aftercare is essential for the best outcomes. It involves following medical advice closely and attending follow-up appointments. This helps ensure that the artery heals properly and maintains improved blood flow.
Atherectomy vs. Other Peripheral Artery Treatments
Atherectomy is just one option among various treatments for peripheral artery disease (PAD). It is especially useful when plaque buildup is complex or resistant to other interventions. Compared to angioplasty or stenting, atherectomy directly removes plaque, which can be advantageous in certain cases.
When considering peripheral artery treatment, it’s important to understand the differences:
- Atherectomy: Removes plaque directly from arteries.
- Angioplasty: Opens narrowed arteries by inflating a balloon.
- Stenting: Keeps arteries open with a small mesh tube.
Each treatment has unique benefits and risks. Your healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate option based on your condition and needs.
Is Atherectomy Right for You?
Determining if atherectomy is suitable involves careful consideration of your specific medical condition. Discussing with a healthcare provider is crucial to understanding the best treatment path for your peripheral artery disease.
Moving Forward with PAD Treatment
Atherectomy provides an effective, minimally invasive option for patients managing peripheral artery disease, helping to restore blood flow and improve quality of life. Compared to traditional surgery, it offers a gentler approach with promising outcomes.
Deciding on the right treatment should be a collaborative process with your healthcare team. At United Vein & Vascular Centers, we are here to guide you every step of the way, ensuring you have the information and support needed to make confident choices for your vascular health.
Schedule a consultation today to explore whether atherectomy is the right option for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Atherectomy is a minimally invasive procedure that removes plaque from narrowed arteries, restoring healthy blood flow and helping reduce pain and complications associated with peripheral artery disease.
Patients with PAD who haven’t responded to medications, angioplasty, or stenting may be ideal candidates. A vascular specialist evaluates each case to determine the safest and most effective approach.
Atherectomy can improve circulation, reduce symptoms, and support a more active lifestyle. While generally safe, risks may include bleeding, artery damage, or infection, which your healthcare team will review before treatment.


