Contents
- What Are Uterine Fibroids?
- What Is Fibroid Degeneration?
- Why Do Fibroids Degenerate?
- Types of Fibroid Degeneration
- Common Symptoms of Fibroid Degeneration
- Fibroid Degeneration After Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
- Managing Symptoms and When to Seek Help
- Potential Complications and Recovery Expectations
- Fibroid Degeneration and Fertility Considerations
- Moving Forward With Confidence in Your Care
- Frequently Asked Questions
Uterine fibroids are a common condition that many women experience at some point in their lives. While these growths are non-cancerous, they can lead to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms that impact daily life. One aspect of fibroid care that’s often misunderstood is fibroid degeneration, a natural process that occurs when a fibroid loses its blood supply and begins to break down.
This process can sometimes cause sudden pain or other symptoms, whether it happens on its own or as part of treatment. For example, Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a minimally invasive procedure designed to block blood flow to the fibroid, which can trigger controlled degeneration and help the fibroid shrink over time.
During this period, it’s common to experience temporary side effects like pain, mild fever, or swelling. Knowing what to expect — and staying in close communication with your healthcare provider — can make recovery smoother and less stressful. Because fibroid degeneration can also affect your menstrual cycle and, in some cases, fertility, a personalized evaluation is key. Your provider can help determine the best course of care to relieve symptoms and support your long-term reproductive health.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are benign growths that develop in the uterus. They are made of muscle and fibrous tissue. These growths are quite common among women of childbearing age.
Though fibroids are non-cancerous, they can cause various symptoms. Some women might not even realize they have fibroids. For others, symptoms can significantly affect their daily lives.
Fibroids vary in size and location. They can range from tiny, undetectable lumps to large masses. Their location can be within the uterine wall, inside the cavity, or on the outer surface.
Common signs of fibroids include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain and pressure
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
It’s crucial for women experiencing symptoms to seek medical advice. An accurate diagnosis can help in managing the condition effectively. Many treatment options are available, depending on individual needs and symptoms.
What Is Fibroid Degeneration?
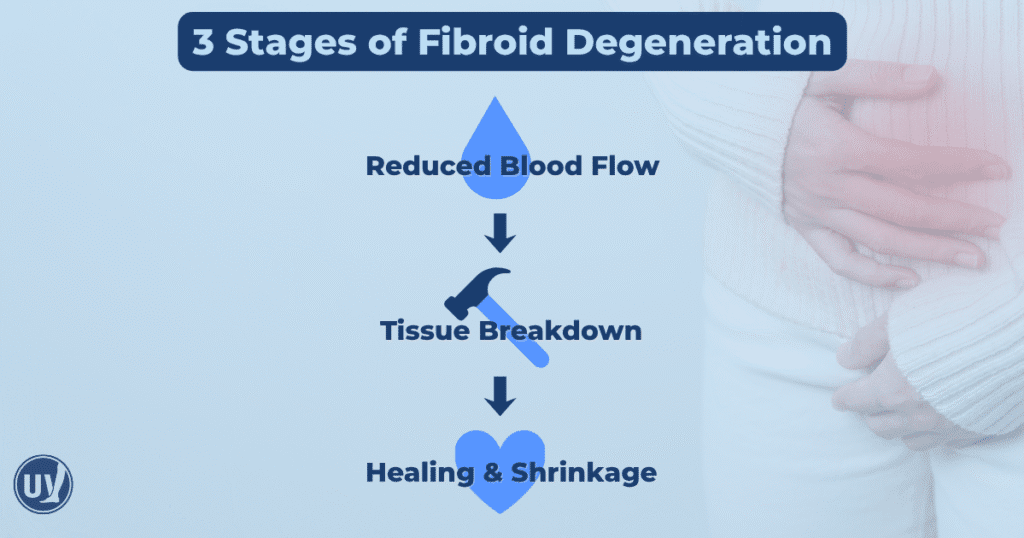
Fibroid degeneration occurs when a fibroid’s blood supply diminishes, leading to tissue breakdown. This process is often a natural part of a fibroid’s life cycle. As fibroids grow, they can outpace their blood supply, resulting in degeneration.
When degeneration happens, fibroids can cause sudden, intense symptoms. These symptoms differ from regular fibroid issues, as they often include sharp pain and inflammation. Understanding the breakdown process can help manage expectations and symptoms effectively.
There are several types of fibroid degeneration, each with unique characteristics. Not every woman with fibroids will experience degeneration, but those who do often report distinct symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms early can guide timely medical intervention and treatment.
Symptoms of fibroid degeneration might include:
- Sudden onset of sharp, localized pain
- Low-grade fever
- Swelling or tenderness in the pelvic area
Timely evaluation of these symptoms by a healthcare provider is crucial. A proper diagnosis can help in choosing the most appropriate treatment options. Medical evaluation can also provide reassurance and guidance during this temporary phase. Understanding these dynamics aids in easing concerns about fibroid degeneration.
Why Do Fibroids Degenerate?
Fibroids degenerate mainly due to insufficient blood supply. As they grow, fibroids require more blood than the body can deliver. This leads to tissue breakdown, known as degeneration.
Several factors contribute to the degeneration of fibroids. One common reason is rapid fibroid growth, which outpaces blood supply. Another factor is pregnancy, during which hormonal changes can impact fibroid blood flow.
Key triggers for fibroid degeneration include:
- Rapid growth exceeding blood supply
- Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy
- Changes in body chemistry or nutrition levels
Understanding these triggers can help in anticipating and managing degeneration-related symptoms. Recognizing the causes enables proactive care and better treatment planning. With this knowledge, patients can engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers. This ensures a tailored, effective approach to managing fibroids.
Types of Fibroid Degeneration
Fibroid degeneration can occur in several forms, each with distinct characteristics. Understanding these types can aid in identifying symptoms and choosing appropriate treatments.
The most common type is hyaline degeneration. It involves fibroids hardening due to the conversion of fibrous tissue. This form is generally not painful and often goes unnoticed without medical imaging.
Another type is red degeneration, often seen during pregnancy. It results from a sudden loss of blood supply, causing acute pain and swelling. This type is usually temporary but can cause significant discomfort.
Three other forms include:
- Cystic degeneration: fluid-filled sacs form within the fibroid
- Myxoid degeneration: softening due to mucous-like fluid accumulation
- Calcification: fibroid tissues harden with calcium deposits over time
Each form of degeneration has unique implications for symptoms and management. Knowing the specific type helps patients tailor their self-care strategies. Engaging healthcare providers in these discussions provides comprehensive support and guidance. Understanding these nuances empowers women navigating fibroid-related challenges.
Common Symptoms of Fibroid Degeneration
Fibroid degeneration is often marked by acute and sometimes unexpected symptoms. Recognizing these can facilitate prompt medical attention and relief.
One key symptom is acute pelvic pain. It can range from mild to severe, often localized where the fibroid is degenerating. This pain might be accompanied by swelling or tenderness in the abdominal area.
Fever is another potential symptom. It indicates an inflammatory response as the body reacts to the breakdown of fibroid tissue. While this can be unsettling, it’s a common part of the degeneration process.
Some women might notice changes in menstrual patterns. These can include heavier or longer periods. This change may point to the presence of degenerating fibroids.
Typical symptoms to watch for include:
- Pelvic pain or cramping
- Abdominal swelling or bloating
- Fever or chills
- Changes in menstrual flow
Being aware of these symptoms ensures that women can seek medical advice when needed. This proactive approach helps in managing discomfort and prevents complications.
Fibroid Degeneration After Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Fibroid degeneration commonly occurs after undergoing Uterine Fibroid Embolization. This minimally invasive procedure targets uterine fibroids by cutting off their blood supply. As blood flow decreases, fibroids gradually shrink and degenerate.
The process of degeneration is integral to UFE’s success. As the fibroids lose their blood supply, they enter a phase of degeneration, leading to shrinkage and symptom relief. Patients often experience temporary symptoms during this process, similar to spontaneous fibroid degeneration.
Symptoms experienced post-UFE might include pelvic pain and cramping. These arise as the fibroid tissue breaks down and are generally short-lived. Some women might also notice changes in their menstrual cycle as their body adjusts to the fibroids’ reduced size.
Common post-UFE symptoms can include:
- Pelvic discomfort or cramps
- Changes in menstrual cycles
- Mild fever or fatigue
While these symptoms might be uncomfortable, they usually improve as the body adapts. Understanding this phase helps patients manage expectations and facilitates recovery. Consulting healthcare providers about concerns or persistent symptoms is important during the post-UFE period.
Managing Symptoms and When to Seek Help
Managing symptoms of fibroid degeneration requires a proactive approach. Simple strategies can ease discomfort during this phase. Over-the-counter pain relievers often help in alleviating cramping or pelvic pain.
Resting and applying heat can further soothe aches and tension. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy diet supports overall well-being and recovery. However, it’s crucial to be aware of more serious signs.
Seek medical advice if pain becomes severe or if a fever persists. Heavy bleeding or unusual changes in menstrual patterns also warrant professional consultation. Effective symptom management empowers patients to navigate the degeneration process confidently.
Key signs to watch for include:
- Severe or persistent pain
- Heavy or unusual bleeding
- Ongoing fever or fatigue
Consulting with your healthcare provider ensures timely intervention and support. Open communication about symptoms enhances care and peace of mind.
Potential Complications and Recovery Expectations
Understanding potential complications of fibroid degeneration is crucial. Although many experience manageable symptoms, some may face challenges. Rarely, severe pain or infection might occur.
Paying attention to how your body responds during recovery is one of the best ways to stay on track. If new or worsening symptoms appear, reach out to your healthcare provider right away. Early communication can make a big difference in your comfort and healing process. Staying open and proactive with your care team helps ensure any concerns are addressed quickly, leading to a smoother, more confident recovery.
Recovery expectations vary among individuals. Most find symptoms subside within a few weeks. During this time, emotional support can be beneficial.
Understanding recovery helps manage expectations and minimize stress.
Fibroid Degeneration and Fertility Considerations
Fibroid degeneration can sometimes impact fertility, but this is not always the case. The impact depends on several factors including fibroid location and size. Understanding these influences helps in planning for conception.
It’s important to discuss fertility goals with your healthcare provider. They can offer tailored advice based on individual circumstances.
Key considerations include:
- Fibroid location affecting uterine lining
- Size impacting uterine shape
- Overall reproductive health
Exploring these factors can guide expectations and choices.
Moving Forward With Confidence in Your Care
Understanding fibroid degeneration helps you take an active role in your health. Staying informed about symptoms, treatment options, and recovery can ease concerns and support better outcomes.
Key points to remember:
- Fibroid degeneration is a natural process that can occur after UFE.
- Symptoms may include pain, cramping, or changes in your menstrual cycle.
- UFE provides an effective, non-surgical option for treating fibroids, with follow-up care to support healing.
If you’re experiencing symptoms or have questions about fibroid treatment, the specialists at United Vein & Vascular Centers are here to help.
Schedule a consultation today to discuss your options and find relief with expert, compassionate care.
Frequently Asked Questions
Most patients experience discomfort, cramping, or mild fever for a few days to a week following UFE. These symptoms typically improve as the body adjusts and the fibroid tissue breaks down. Your healthcare provider may recommend pain relief strategies and rest to support recovery.
Yes. Fibroid degeneration can occur naturally when a fibroid outgrows its blood supply. This spontaneous degeneration can cause sudden pelvic pain or changes in menstrual flow, but symptoms usually resolve once the fibroid stabilizes.
You should reach out to your vascular specialist if you experience severe or persistent pelvic pain, heavy bleeding, or fever that doesn’t subside. These could indicate complications that require medical attention.