Contents
- What Are Uterine Fibroids?
- What Is Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
- What Is a Hysterectomy?
- Comparing Effectiveness and Outcomes
- Recovery: What to Expect
- Fertility and Hormonal Considerations
- Risks and Side Effects
- Who Is a Good Candidate for UFE?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Take Control of Your Fibroid Treatment Options
If you have been diagnosed with uterine fibroids, you may already know how disruptive they can be. Heavy bleeding. Pelvic pressure. Pain that interferes with work, exercise, and sleep. For many women, fibroids are more than a nuisance. They can take over daily life.
When symptoms become difficult to manage, treatment becomes necessary. Two of the most commonly recommended options are Uterine Fibroid Embolization, known as UFE, and hysterectomy.
Both treatments can provide relief. However, they are very different procedures with very different long term implications. Understanding those differences is essential so you can choose the approach that aligns with your health goals, lifestyle, and future plans.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus. They vary in size, number, and location. Some are as small as a seed, while others can grow large enough to enlarge the abdomen.
Many women with fibroids experience no symptoms. But for others, fibroids can cause:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Pain during intercourse
- Abdominal bloating
Fibroids are influenced by hormones and commonly develop during reproductive years. While they are not cancerous, they can significantly impact quality of life.
When symptoms start to disrupt your daily routine or limit your activities, it may be time to consider treatment options.
What Is Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
Uterine Fibroid Embolization is a minimally invasive, image guided procedure performed by a vascular specialist.
Instead of removing fibroids surgically, UFE works by cutting off their blood supply. Fibroids rely on blood flow to grow and survive. When that blood supply is reduced, the fibroids shrink over time.
Here is how the procedure works:
A small catheter is inserted through a tiny puncture in the wrist or groin. Using advanced imaging, the physician guides the catheter to the uterine arteries that supply blood to the fibroids. Tiny particles are then injected to block that blood flow.
Without an adequate blood supply, fibroids begin to slowly shrink over time, and as they do, many patients notice meaningful relief from the symptoms that once disrupted their daily lives.
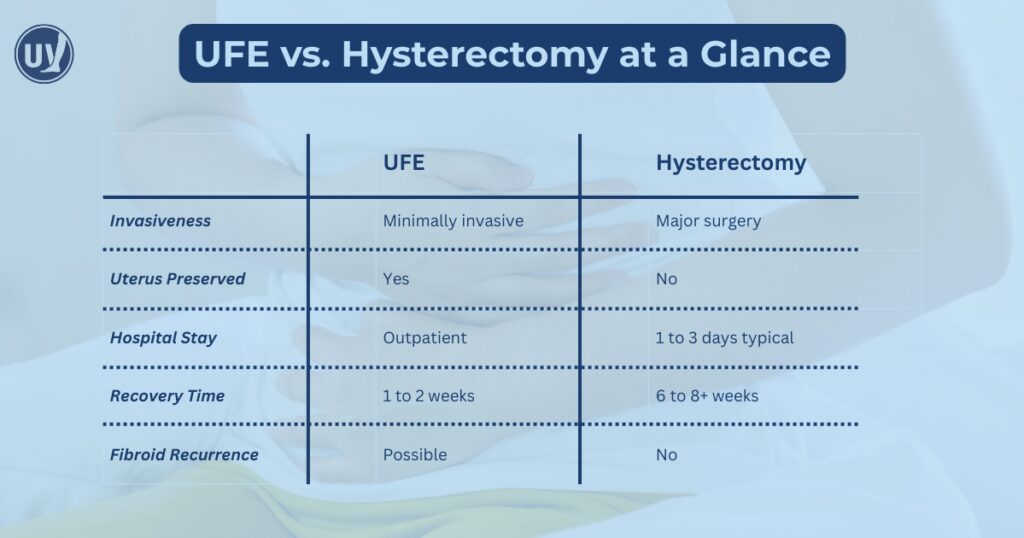
UFE is performed in an outpatient setting and is minimally invasive, meaning it does not require large surgical incisions or an extended hospital stay, allowing most patients to return home the same day.
What Is a Hysterectomy?
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the uterus. In some cases, the cervix and ovaries may also be removed.
Because the uterus is removed entirely, fibroids cannot return. This makes hysterectomy a definitive treatment for uterine fibroids.
There are different types of hysterectomy:
- Abdominal hysterectomy, which involves a larger incision
- Vaginal hysterectomy
- Laparoscopic or robotic assisted hysterectomy
Recovery time depends on the surgical method and the patient’s overall health. Hospital stays and longer recovery periods are common, particularly with abdominal surgery.
It is important to note that hysterectomy permanently ends fertility.
Comparing Effectiveness and Outcomes
Both UFE and hysterectomy are effective at relieving fibroid symptoms. The difference lies in how they achieve that relief and what it means for your future.
UFE:
- Shrinks fibroids rather than removing them
- Preserves the uterus
- Significantly reduces heavy bleeding and pelvic pain in most patients
- Allows for a quicker return to normal activities
Hysterectomy:
- Completely removes the uterus
- Eliminates fibroids permanently
- Prevents recurrence
- Requires longer recovery
For many women, symptom relief is the primary goal. UFE has been shown to provide substantial improvement in bleeding, pressure, and pain for the majority of patients.
Your medical history, fibroid size, and overall health will influence which option is most appropriate.
Recovery: What to Expect
Recovery is often one of the most important deciding factors.
UFE Recovery
Most women go home the same day. Cramping and mild discomfort are common for a few days but are manageable with medication. Many patients return to light activities within several days and resume normal routines within one to two weeks.
Hysterectomy Recovery
Recovery from hysterectomy can take several weeks, especially if an abdominal incision is required. Activity restrictions are more significant, and full healing may take six to eight weeks or longer.
For women balancing work, family, and other responsibilities, recovery time can play a major role in treatment decisions.
Fertility and Hormonal Considerations
Fertility is another key factor when comparing UFE and hysterectomy.
UFE preserves the uterus, which may allow for future pregnancy. However, women who plan to become pregnant should have a detailed discussion with their physician about timing and individual risks.
Hysterectomy permanently removes the uterus, eliminating the possibility of carrying a pregnancy. If the ovaries are removed, hormonal changes and early menopause may occur.
For women who have completed their families or are not concerned about fertility, hysterectomy may feel like a straightforward solution. For others, preserving the uterus is an important priority.
Risks and Side Effects
All medical procedures carry risks, though serious complications are uncommon.
UFE Risks
- Temporary pelvic pain or cramping
- Mild nausea or fatigue
- Rare risk of infection
UFE avoids large incisions and general anesthesia in many cases, reducing surgical risk.
Hysterectomy Risks
- Infection or bleeding
- Surgical complications
- Longer recovery
- Possible hormonal changes
Understanding these differences helps patients feel more confident in their decision.
Who Is a Good Candidate for UFE?
UFE may be a good option for women who:
- Experience heavy menstrual bleeding due to fibroids
- Have pelvic pain or pressure
- Want to avoid major surgery
- Prefer to preserve their uterus
- Are seeking a minimally invasive solution
A consultation with a vascular specialist can determine whether fibroid size, location, and overall health make you a candidate.
Frequently Asked Questions
UFE provides significant symptom relief for most women and avoids major surgery. While hysterectomy permanently eliminates fibroids, many patients achieve lasting improvement with UFE without removing the uterus.
Most women recover from UFE within one to two weeks. Hysterectomy recovery can take six to eight weeks or longer depending on the surgical method.
UFE shrinks existing fibroids and significantly reduces symptoms. While new fibroids can develop over time, many women experience long term relief and do not require additional treatment.
Take Control of Your Fibroid Treatment Options
You do not have to live with heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, or pressure caused by uterine fibroids. And you do not have to assume that major surgery is your only option.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization offers a minimally invasive alternative that preserves the uterus while delivering meaningful symptom relief.
At United Vein and Vascular Centers, our experienced specialists provide advanced, image guided UFE treatment in a comfortable outpatient setting. We take the time to understand your symptoms, your goals, and your long term health priorities.
If fibroids are affecting your quality of life, schedule a consultation today. Find a United Vein and Vascular Centers location near you and explore whether UFE is the right solution for lasting relief.

